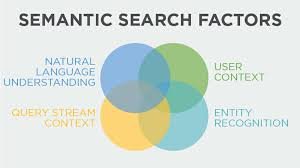
Semantic SEO is the practice of optimizing content for meaning and user intent rather than exact keywords. It aligns with the shift of search engines—especially Google—toward interpreting queries through entities, context, and user need. Semantic SEO ensures content corresponds to what users mean when they search, not just the words they input.
Google has openly stated that search algorithms now focus on understanding language and meaning, as described in their Search Central guidelines. This shift is designed to help users receive the most relevant and accurate information, not just pages repeating the keywords they typed.
Longer queries like spoken voice searches or multi-part questions are handled better due to semantic understanding. With developments like Google’s Hummingbird, RankBrain, and BERT, and more recently MUM, semantic SEO has become essential for ranking well.
What Is Semantic SEO?
Semantic SEO involves creating content that conveys clear meaning and context, aligning closely with user intent. Unlike traditional keyword-based SEO, it focuses on related concepts, synonyms, and real-world entities.
Google’s use of the Knowledge Graph allows the search engine to connect facts about people, places, and things, enhancing its understanding of topics. For example, a page about the “Eiffel Tower” can gain relevance by also mentioning related entities like “Paris,” “France,” and “tourism,” helping Google connect these pieces of information meaningfully.
Structured data and semantic markup, such as Schema.org vocabulary, help search engines interpret content beyond keywords, making it easier to match pages to user intent.
The Evolution of Search Engines Toward Semantic Understanding
Search engines have evolved significantly in recent years, moving from exact keyword matching to understanding meaning:
- Hummingbird (2013): A rewrite of Google’s algorithm designed to better understand conversational search queries.
- RankBrain (2015): A machine-learning system that interprets unfamiliar or ambiguous queries by understanding patterns and context.
- BERT (2018): A breakthrough in natural language processing (NLP) that allows Google to interpret meaning based on word order and relationships, not just keywords. You can learn more about this approach in the BERT research paper on arXiv.
- MUM (2021): A multimodal model capable of understanding information across different languages and formats, making search more intuitive and context-driven.
These advancements demonstrate the continuous shift toward semantic interpretation, allowing users to find answers even without using precise keywords.
How Semantic SEO Works
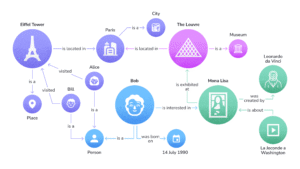
Semantic SEO uses entities, context, and structured data to make content easier for search engines to interpret. Google identifies entities and their salience within a webpage using technologies similar to those in its Natural Language API.
The process works through:
- Topic Clustering: Organizing related content around pillar topics to show depth and relevance.
- Entity Identification: Recognizing named entities like organizations, locations, and events.
- Structured Data: Adding schema markup to help crawlers understand content meaningfully (Schema.org documentation).
- Internal Linking: Connecting related pages to strengthen semantic relationships.
This approach allows content to rank for a broader set of relevant queries and appear in enhanced search results like featured snippets and knowledge panels.
Benefits of Semantic SEO for Websites
Semantic SEO provides several advantages:
- Improved relevance: Helps your content appear for queries related to the topic, not just the exact keyword.
- Better performance for voice search: Optimized content aligns with how people speak rather than type.
- Enhanced SERP features: Structured data can lead to rich results, increasing visibility.
- User experience improvements: Detailed, well-structured content keeps visitors engaged.
- Authority building: Factual, entity-based content aligns with Google’s E-A-T guidelines on expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness.
| Benefit | Description |
| Broader query coverage | Ranks for multiple intent-based queries |
| Voice & conversational | Matches spoken language searches |
| Rich SERP features | Eligible for snippets, panels, and other enhanced results |
| Improved engagement | Reduces bounce rates, increases session duration |
| Authority and trust | Strengthens credibility through high-quality, structured data |
Key Elements of a Semantic SEO Strategy
An effective semantic SEO strategy includes:
- Topic Clusters: Organizing pages around core subjects and related subtopics for depth and clarity.
- Contextual Keywords: Using synonyms and related terms naturally to convey meaning without stuffing.
- Internal Linking: Structuring site navigation to reflect topic relationships.
- Schema Markup: Applying structured data as defined in Schema.org to provide context for crawlers.
- Entity Salience: Highlighting important entities consistently to ensure they are recognized as central themes.
- Content Depth: Providing comprehensive, well-researched information backed by reliable sources.
When applied consistently, these elements signal to search engines that your content is authoritative, relevant, and contextually rich.
How Search Engines Interpret Semantic Signals
Search engines process semantic signals through a combination of machine learning and natural language understanding. According to Google’s Search documentation:
- Entities are identified and analyzed for relevance and importance.
- Contextual relationships between words and phrases determine meaning beyond keyword matching.
- Link structures establish topical connections between pages.
- Structured data provides machine-readable context, improving understanding and SERP features.
- Trust and authority signals from reliable sources influence ranking.
These factors allow search engines to determine how well a page satisfies the user’s intent, not just whether it contains matching keywords.
Tools and Resources for Implementing Semantic SEO
To implement semantic SEO effectively, you can use:
- Google Search Console: For monitoring how Google interprets and indexes your content (Search Console overview).
- Google’s Search Quality Evaluator Guidelines: A detailed guide on how content is assessed for expertise, trustworthiness, and relevance (official guidelines).
- Schema Markup Libraries: The Schema.org vocabulary provides standardized markup for structured data.
- Google Natural Language API: Helps analyze text to see entities and salience scores (documentation).
- Arxiv and academic resources: For understanding the technical background of semantic algorithms, such as the BERT research paper.
These tools ensure that your website content is machine-readable, intent-focused, and contextually complete.
Best Practices for Creating Semantic SEO-Friendly Content
When writing content optimized for semantic SEO:
- Focus on topics instead of isolated keywords, covering related entities and concepts naturally.
- Use clear heading structures to organize information logically.
- Implement FAQ schema to answer common user questions in a structured format.
- Include factual data and cite reputable sources, enhancing credibility.
- Keep entity names consistent across pages.
- Follow Google’s recommendations in the Search Essentials for clarity and quality.
- Write in a reader-friendly style, with short sentences, bullet points, and scannable paragraphs.
This approach improves both user experience and search engine interpretation, leading to stronger long-term rankings.
Future of Semantic SEO and AI-Powered Search
The future of SEO lies in AI and semantic understanding. Google’s MUM technology and advancements in large language models are making search engines more capable of understanding complex, conversational queries.
Expect developments such as:
- Conversational search dominance, requiring natural, dialogue-like content.
- Cross-language information retrieval, as models interpret meaning beyond single-language boundaries.
- Enhanced AI summaries, where search engines may synthesize information from multiple sources.
- Increased reliance on structured data, entity linking, and factual accuracy.
Websites adopting semantic SEO now are future-proofing their content for evolving AI-driven search environments.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Semantic SEO
Key mistakes include:
- Keyword stuffing, focusing on frequency over meaning.
- Ignoring structured data, which limits how search engines understand context.
- Publishing thin, disconnected content, lacking depth and relationships.
- Inconsistent entity naming, reducing clarity in topic recognition.
- Neglecting user intent, producing irrelevant or unhelpful content.
Avoiding these ensures a solid, meaning-first SEO strategy that aligns with search engine advancements.
Final Thoughts on Semantic SEO
Semantic SEO is essential in today’s search landscape, focusing on meaning, entities, and context rather than keyword matching. By aligning content with Google’s quality standards, using structured data, and optimizing for intent, you improve visibility, user experience, and long-term search success.
Adopting a semantic-first strategy ensures that your website stays relevant as search engines evolve toward AI-powered, intent-driven results.